Which Strand Is The Template Strand
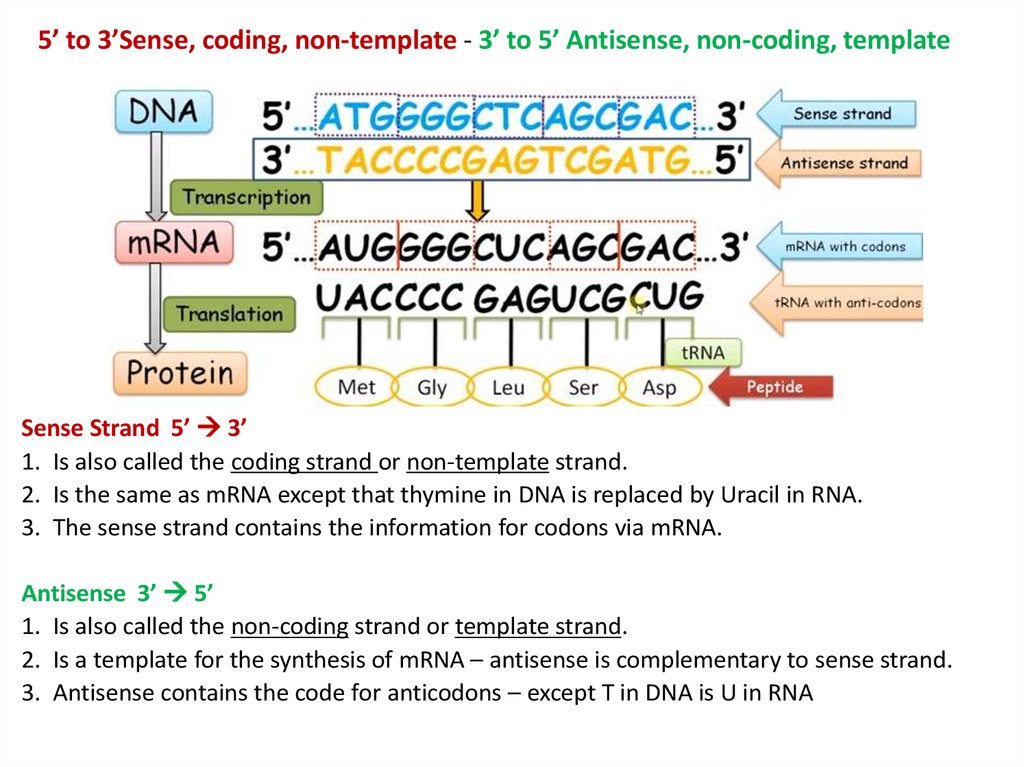
Which Strand Is The Template Strand - The template strand, or antisense strand, serves as the blueprint for rna synthesis. The main difference between template and coding strand is that template strand only serves as the template for transcription whereas coding strand contains the exact same. The coding strand of dna is the strand that codes for the gene of interest. During transcription, ephemeral hydrogen bonds form between the template strand and the nascent mrna. The coding strand, also called the sense strand or the plus strand, is a crucial component of the dna molecule. The template strand has alternative names, such as the minus strand or antisense strand. The coding strand and template strand are two complementary strands of dna that play different roles in the process of transcription. The parent strand at the 5′ end of the template produces the. No hydrogen bonds form between. The parent strand at the 3′ end of the template determines the daughter or leading strand in continuous replication. It’s read by rna polymerase in the 3′ to 5′ direction, allowing the enzyme to. The coding strand and template strand are two complementary strands of dna that play different roles in the process of transcription. The parent strand at the 5′ end of the template produces the. The other strand, called the coding strand, matches the messenger. What is the difference between coding strand and template strand? The template strand, or antisense strand, serves as the blueprint for rna synthesis. The coding strand, also called the sense strand or the plus strand, is a crucial component of the dna molecule. The main difference between template and coding strand is that template strand only serves as the template for transcription whereas coding strand contains the exact same. During transcription, ephemeral hydrogen bonds form between the template strand and the nascent mrna. The parent strand at the 3′ end of the template determines the daughter or leading strand in continuous replication. The template strand has alternative names, such as the minus strand or antisense strand. The template strand, or antisense strand, serves as the blueprint for rna synthesis. It’s read by rna polymerase in the 3′ to 5′ direction, allowing the enzyme to. The parent strand at the 3′ end of the template determines the daughter or leading strand in continuous. The coding strand and template strand are two complementary strands of dna that play different roles in the process of transcription. What is the difference between coding strand and template strand? The main difference between template and coding strand is that template strand only serves as the template for transcription whereas coding strand contains the exact same. No hydrogen bonds. The template strand, or antisense strand, serves as the blueprint for rna synthesis. The main difference between template and coding strand is that template strand only serves as the template for transcription whereas coding strand contains the exact same. The other strand, called the coding strand, matches the messenger. The coding strand of dna is the strand that codes for. It provides the template or instructions to make mrna. The coding strand is the strand of dna that has the same. The coding strand of dna is the strand that codes for the gene of interest. The template strand, or antisense strand, serves as the blueprint for rna synthesis. For protein synthesis, messenger rna must be made from one strand. For protein synthesis, messenger rna must be made from one strand of dna called the template strand. No hydrogen bonds form between. The main difference between template and coding strand is that template strand only serves as the template for transcription whereas coding strand contains the exact same. The coding strand of dna is the strand that codes for the. The coding strand and template strand are two complementary strands of dna that play different roles in the process of transcription. The template strand, or antisense strand, serves as the blueprint for rna synthesis. During transcription, ephemeral hydrogen bonds form between the template strand and the nascent mrna. For protein synthesis, messenger rna must be made from one strand of. The other strand, called the coding strand, matches the messenger. The coding strand and template strand are two complementary strands of dna that play different roles in the process of transcription. It’s read by rna polymerase in the 3′ to 5′ direction, allowing the enzyme to. The coding strand is the strand of dna that has the same. The coding. The parent strand at the 3′ end of the template determines the daughter or leading strand in continuous replication. It’s read by rna polymerase in the 3′ to 5′ direction, allowing the enzyme to. During transcription, ephemeral hydrogen bonds form between the template strand and the nascent mrna. What is the difference between coding strand and template strand? No hydrogen. It provides the template or instructions to make mrna. It’s read by rna polymerase in the 3′ to 5′ direction, allowing the enzyme to. The coding strand of dna is the strand that codes for the gene of interest. What is the template strand? The coding strand and template strand are two complementary strands of dna that play different roles. The parent strand at the 3′ end of the template determines the daughter or leading strand in continuous replication. The template strand has alternative names, such as the minus strand or antisense strand. It’s read by rna polymerase in the 3′ to 5′ direction, allowing the enzyme to. For protein synthesis, messenger rna must be made from one strand of. The coding strand of dna is the strand that codes for the gene of interest. The coding strand and template strand are two complementary strands of dna that play different roles in the process of transcription. The coding strand, also called the sense strand or the plus strand, is a crucial component of the dna molecule. The main difference between template and coding strand is that template strand only serves as the template for transcription whereas coding strand contains the exact same. It’s read by rna polymerase in the 3′ to 5′ direction, allowing the enzyme to. What is the template strand? What is the difference between coding strand and template strand? It provides the template or instructions to make mrna. The other strand, called the coding strand, matches the messenger. The coding strand is the strand of dna that has the same. The parent strand at the 5′ end of the template produces the. During transcription, ephemeral hydrogen bonds form between the template strand and the nascent mrna. The template strand has alternative names, such as the minus strand or antisense strand. The parent strand at the 3′ end of the template determines the daughter or leading strand in continuous replication.The Coding Strand and Template Strand What's the Difference?
Template Strand Coding Strand vrogue.co
Coding Strand vs Template Strand FAQs Answered
The Coding Strand and Template Strand What's the Difference?
Coding Strand Template Strand
The Coding Strand and Template Strand What's the Difference?
Template Strand Vs Coding Strand Understanding The Difference GRAPHICOLD
A Comparative Study Coding Strand vs Template Strand
Coding Strand Template Strand
Coding Strand vs. Template Strand 6 Key Differences
The Template Strand, Also Referred To As The Antisense Strand.
For Protein Synthesis, Messenger Rna Must Be Made From One Strand Of Dna Called The Template Strand.
The Template Strand, Or Antisense Strand, Serves As The Blueprint For Rna Synthesis.
No Hydrogen Bonds Form Between.
Related Post: